Subaquatic Barotrauma: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments to Protect Your Ears
|| ScubaLiveTV || Insights || Actuality || Interviews || TV Web || History || Scuba Diving || Freediving || Video collection || Nature and Environment || Collaborate with us ||
Subaquatic Barotrauma: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments to Protect Your Ears
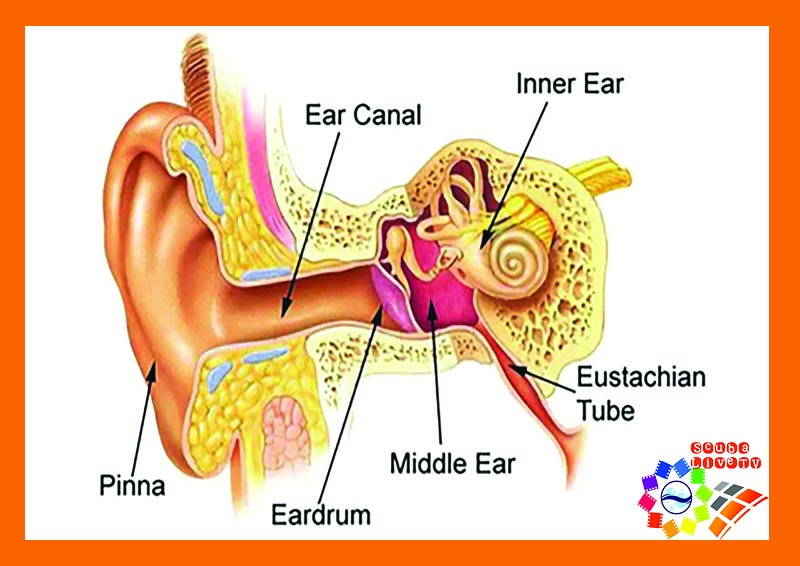
Subaquatic barotrauma to the ear, also known as middle ear barotrauma, is a common injury that can occur during scuba diving due to changes in pressure. It happens when the air pressure inside the middle ear fails to equalize properly with the surrounding environment.
Causes:
Subaquatic barotrauma to the ear is primarily caused by a difference in pressure between the middle ear and the external environment during descent or ascent in water. During descent, water pressure increases and can exert force on the eardrum. If the air pressure in the middle ear is not properly regulated, a pressure difference can occur, leading to damage.
One of the main causes of barotrauma is the failure to equalize pressure. Equalization is a process that balances the air pressure in the middle ear with the surrounding environment. During scuba diving, it is essential to regularly and correctly equalize the pressure during descent to prevent ear damage.
Several factors can hinder pressure equalization, such as obstruction to airflow through the nose or throat. This can happen due to a cold, nasal congestion, or upper respiratory infections. It is important to ensure that the upper airways are clear and there are no obstacles impeding airflow during equalization.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of middle ear barotrauma can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Ear pain is one of the most common symptoms and can range from mild to intense. It can occur during descent or ascent or shortly after diving. Other symptoms include a sensation of plugged ears or temporary hearing loss due to pressure difference, dizziness, and balance problems. In severe cases, bleeding from the ear may occur due to a ruptured eardrum.
Here are some of the common symptoms:
Ear pain: It is one of the most common symptoms. The pain can range from mild to intense and may occur during descent or ascent or shortly after diving.
Plugged ear sensation: You may experience a sensation of plugged ears or temporary hearing loss due to the pressure difference between the middle ear and the outside.
Dizziness and balance problems: Some people may experience dizziness or balance problems following middle ear barotrauma.
Bleeding from the ear: In more severe cases, bleeding from the ear may occur due to a ruptured eardrum.
Treatment:
The treatment for middle ear barotrauma depends on the severity of the injury. Typically, rest and avoiding underwater diving and other activities that could exacerbate the injury are recommended. Rest allows the ear to heal naturally. If the symptoms persist or are particularly severe, it is advisable to consult a doctor or an otolaryngologist. They may prescribe pain medication or medications to reduce inflammation. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged eardrum or correct other problems in the middle ear.
Here are some possible treatment options:
Rest: After middle ear barotrauma, it is advisable to avoid underwater diving and other activities that could exacerbate the injury. Allowing time to heal is essential.
In conclusion, it is always recommended to take precautions to protect the ears during underwater diving and prevent barotrauma. Make sure to equalize ear pressure during descent regularly and correctly. Additionally, avoid diving if you have upper respiratory infections or nasal congestion.









